Specifically it measures the fractional change in size per degree change in temperature at a constant pressure.
Thermal coeffiient expansion marble.
Thermal expansion the change in dimension linear or volumetric of a rock specimen with temperature is expressed in terms of a coefficient of thermal expansion.
Dl expansion in dt temperature differences c or k h heat transfer coefficient w m2.
Heat transfer coefficient from inside h heat transfer coefficient from outside k coefficient of thermal conductivity w m.
Special thanks to reader eric.
Volumetric area and linear.
0 9 to 1 2 x 10 5.
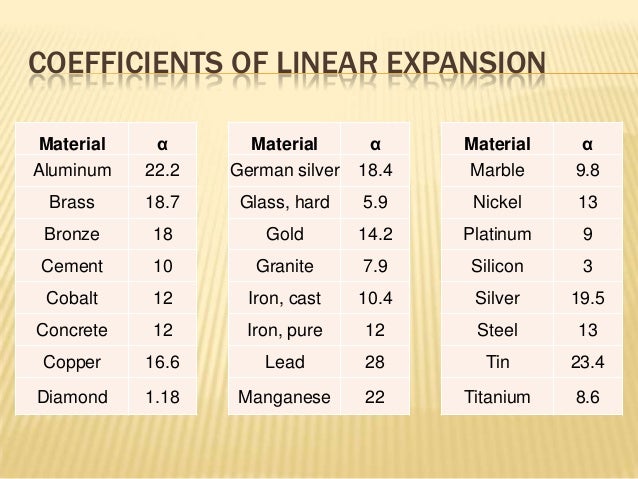
Thermal expansion coefficients for some common materials.
This is given as the ratio of dimension change e g change in volume to the original dimension volume v per unit of temperature t change.
Thermal movement can include temperature fluctuations and changes in environmental temperature.
K l length m q total heat transfer watt q heat flux w m2 r thermal resistance.
The change in volume due to thermal expansion is δ v βv δ t where β is the coefficient of volume expansion and β 3α.
1 2 to 1 3 x 10 5.
The marble institute of america s mia design manual references the tcna detail ej171 for expansion.
10 6 m moc 1 μm moc m m meter per meter in in inches per inches most values for temperature 25 oc 77 of.
Cement concrete sand stone.
This is easy to.
The coefficient of thermal expansion describes how the size of an object changes with a change in temperature.
The coefficient of linear thermal expansion clte of any material is the change of a material s dimension per unit change in temperature.
American elements toolbox of conversion tables properties identifiers and size charts.
The thermal expansion of marble is about the same as granite coefficient of expansion in inches of expansion per inch of material per degree f.
Thermal stress is created when thermal expansion is constrained.
Thermal expansion coefficient of metals materials.
Several types of coefficients have been developed.
Cement concrete quartzite.
Coefficient of expansion x temperature range x distance between joints.